有向グラフに対して行う強連結成分分解を扱うライブラリを整備しました。
強連結成分分解
ABC296E問題(解説記事)で強連結成分分解について紹介しました。
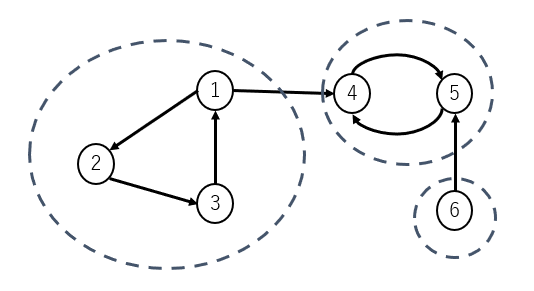
有向グラフにおいて、巡回できる頂点同士を同じグループに分けることを強連結成分分解と呼びます。具体的には、以下の図で示している連結している有向グラフの頂点を、{1, 2, 3}、{4, 5}, {6} のグループに分解します。
分解する基本的な考え方は、以下となります。
- 有向グラフ G に対して、深さ優先探索(DFS)を行い、探索が終わった頂点の順番(order)を格納する。
- 枝を逆向きにした rG に対して、order が大きい頂点から深さ優先探索を行う。ある頂点から探索できる範囲は、同じ連結成分となる。
クラス StronglyConnectedComponents として実装しました。実装はこちらのページを参考にさせていただきました。コードは以下となります。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class StronglyConnectedComponents {
private:
int n;
vector<vector<int>> G, rG;
vector<int> order;
vector<bool> seen;
public:
vector<int> component;
private:
void dfs(int v) {
seen[v] = true;
for (auto next_v : G[v]) {
if (!seen[next_v]) {
dfs(next_v);
}
}
order.push_back(v);
}
void rdfs(int v, int k) {
component[v] = k;
for (auto next_v : rG[v]) {
if (component[next_v] < 0) {
rdfs(next_v, k);
}
}
}
public:
StronglyConnectedComponents(int _n, vector<vector<int>> &_G, vector<vector<int>> &_rG) {
n = _n;
G = _G;
rG = _rG;
component.assign(n, -1);
seen.assign(n, false);
for (int v = 0; v < n; ++v) {
if (!seen[v]) {
dfs(v);
}
}
int k = 0;
reverse(order.begin(), order.end());
for (auto v : order) {
if (component[v] == -1) {
rdfs(v, k);
++k;
}
}
}
bool is_same(int u, int v) {
return component[u] == component[v];
}
};ライブラリのテスト
AIZU ONLINE JUDGE で出題されている問題でアルゴリズムをテストします。以下が問題のリンク先です。
GRL 3_C問題 Strongly Connected Components
この問題を解くプログラムは以下です。AC判定となります。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class StronglyConnectedComponents {
private:
int n;
vector<vector<int>> G, rG;
vector<int> order;
vector<bool> seen;
public:
vector<int> component;
private:
void dfs(int v) {
seen[v] = true;
for (auto next_v : G[v]) {
if (!seen[next_v]) {
dfs(next_v);
}
}
order.push_back(v);
}
void rdfs(int v, int k) {
component[v] = k;
for (auto next_v : rG[v]) {
if (component[next_v] < 0) {
rdfs(next_v, k);
}
}
}
public:
StronglyConnectedComponents(int _n, vector<vector<int>> &_G, vector<vector<int>> &_rG) {
n = _n;
G = _G;
rG = _rG;
component.assign(n, -1);
seen.assign(n, false);
for (int v = 0; v < n; ++v) {
if (!seen[v]) {
dfs(v);
}
}
int k = 0;
reverse(order.begin(), order.end());
for (auto v : order) {
if (component[v] == -1) {
rdfs(v, k);
++k;
}
}
}
bool is_same(int u, int v) {
return component[u] == component[v];
}
};
int main()
{
int v, e;
cin >> v >> e;
vector<vector<int>> G(v);
vector<vector<int>> rG(v);
for (int i = 0; i < e; ++i) {
int s, t;
cin >> s >> t;
G[s].push_back(t);
rG[t].push_back(s);
}
StronglyConnectedComponents scc(v, G, rG);
int q;
cin >> q;
for (int i = 0; i < q; ++i) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
if (scc.is_same(u, v)) {
cout << 1 << endl;
} else {
cout << 0 << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}最後に
昔に解いた問題から、ライブラリ化できる部分を切り出して紹介しました。このような記事を書くことを通じて、理解度を上げたいです。





